Is your yard being overrun by Boreal Alopecurus? This aggressive grass species can quickly transform your once-lush lawn into an uneven, patchy landscape. Identifying and managing this invasive species is crucial for maintaining a healthy yard.
In this article, we’ll explore what Boreal Alopecurus is, how to recognize its presence, effective removal techniques, and strategies for prevention.
What is Boreal Alopecurus?
Boreal Alopecurus, scientifically known as Alopecurus alpinus, is a perennial grass native to colder regions. It is notorious for its rapid growth and ability to form dense clumps that can easily outcompete and choke out desirable grass species in your lawn.
Its aggressive nature is primarily fueled by its early spring seed production, making it challenging to control once it takes hold.

Key Characteristics:
Growth Habit
Boreal Alopecurus is a perennial grass known for its robust growth pattern. It typically forms dense clumps that can reach 12 to 24 inches (30 to 60 cm). These clumps can spread aggressively, making it a formidable competitor against desirable lawn grasses.
- Clumping Nature: The grass tends to grow in tufted formations, which can create an uneven appearance in lawns. Its dense growth can smother neighboring plants and limit their access to sunlight, water, and nutrients.
Leaf Characteristics
The leaves of Boreal Alopecurus are one of its most distinguishing features.
Color
The leaves are typically a deep, rich green, but they can also appear lighter in certain conditions, making them stand out against other grass types.
Shape and Size
The leaves are narrow and elongated, usually measuring about 1/4 inch wide. They can be slightly ribbed and are often folded along the midrib, which gives them a distinctive look.
Texture
When healthy, leaf blades have a smooth texture and tend to be soft to the touch, contributing to their aesthetic appeal.
Seed Heads
Boreal Alopecurus produces characteristic seed heads that play a critical role in its reproduction and spread.
- Formation: The seed heads are elongated and resemble foxtails. They usually emerge in late spring to early summer and can reach lengths of 4 to 10 inches (10 to 25 cm).
- Color: The seed heads start as a greenish hue and turn golden-brown as they mature. This color change can make them easily recognizable.
- Seed Production: Each seed head can produce numerous seeds, which are dispersed by wind and water, contributing to this species’ rapid spread.
Root System
Boreal Alopecurus has a well-developed root system that enhances its competitiveness.
Root Depth

The grass has a fibrous root system that extends deep into the soil, allowing it to access moisture and nutrients more effectively than shallow-rooted grasses.
Rhizomatic Growth
While Boreal Alopecurus primarily spreads through seeds, it can also develop rhizomes (horizontal underground stems) in some cases, further aiding its ability to colonize new areas.
Habitat Preferences
Boreal Alopecurus thrives in various environmental conditions, making it adaptable to many landscapes.
- Climate: It is primarily found in cooler regions, which is why it is often seen in northern climates or higher elevations.
- Soil Type: This species prefers moist, well-drained soils but can tolerate a range of soil types, from sandy to clay.
- Sunlight: Boreal Alopecurus thrives in full sun but can also tolerate partial shade, which increases its ability to invade various areas.
Allelopathic Properties
One of the more insidious features of Boreal Alopecurus is its allelopathic behavior.
Chemical Release
This grass releases biochemicals into the soil that can inhibit the growth of nearby plants. This allows it to gain a competitive edge, as it can suppress the growth of desirable grass species and other plants nearby.
Impact on Biodiversity
Boreal Alopecurus’s allelopathic nature can decrease plant diversity in invaded areas, further entrenching its dominance.
Environmental Impact
Boreal Alopecurus can have significant ecological consequences.
- Outcompeting native and desirable grass species reduces plant diversity, which can negatively affect local wildlife that relies on a variety of plants for food and habitat.
- Its dense root system can help stabilize soil, but its ability to dominate can also cause the displacement of native plants that contribute to soil health and structure.
Seasonal Behavior
Boreal Alopecurus exhibits distinct seasonal behavior that can affect management practices.
- Early Germination: This grass typically germinates early in the spring, giving it a head start over slower-growing grass species.
- Growth Cycle: It continues to grow actively throughout the spring and early summer, often dormant during the hotter months but re-emerging as temperatures cool.
How to Identify Boreal Alopecurus in Your Lawn:

Identifying Boreal Alopecurus early is essential for effective management. Look for the following signs:
Dense Clumping
Noticeable clusters of grass that differ from the surrounding turf.
Seed Heads
Foxtail-like spikes are visible by mid to late summer.
Color Variation
Lighter green foliage that stands out against darker grass.
Uneven Growth Patterns
Patchy areas where the grass appears overgrown or sparse.
If you spot these indicators, acting promptly is crucial to prevent further spread.
Read: A Comprehensive Guide of the Power of T202315303YGJ!
The Dangers of Boreal Alopecurus in Your Lawn:
Left unchecked, Boreal Alopecurus can wreak havoc on your lawn. Here’s how:
Outcompetes Desirable Grasses
This invasive species quickly dominates the turf, leading to an unkempt appearance and health deterioration of your lawn.
Disrupts Soil Health
Its extensive root system can interfere with nutrient absorption, harming the overall ecosystem and inviting pests.
Increases Maintenance Costs
The presence of Boreal Alopecurus can lead to higher lawn care expenses due to increased weeding and repair efforts.
Effective Management Strategies for Boreal Alopecurus:
To effectively remove Boreal Alopecurus and restore your lawn, consider the following strategies:
Manual Removal
- Hand-pulling: For small infestations, carefully pull out the grass by the roots to prevent regrowth.
- Raking: Use a rake to collect and dispose of clumps after manual removal.
Herbicide Application
Choose a selective herbicide designed to target Boreal Alopecurus while preserving desirable grass species. Follow the application instructions carefully for optimal results.
Cultural Control
Regular Mowing
Keep your lawn mowed to prevent seed heads from developing, reducing the chances of spreading.
Fertilization and Watering
Maintain a healthy lawn through proper fertilization and watering, encouraging the growth of desirable grass that can outcompete Boreal Alopecurus.
Soil Health Maintenance
- Aeration: Aerate your lawn to improve soil health and promote the growth of beneficial grass species.
- Nutrient Management: Conduct a soil test to determine nutrient deficiencies and apply appropriate amendments.
The Allelopathic Advantage of Boreal Alopecurus:
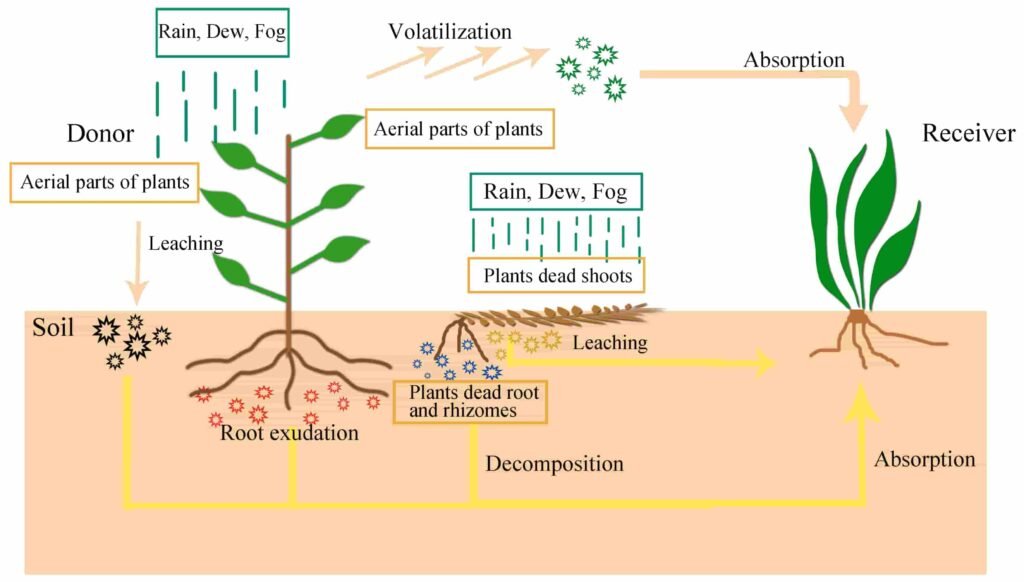
One reason Boreal Alopecurus thrives is its allelopathic behavior. This means it releases biochemicals into the soil that inhibit the growth of neighboring plants, allowing it to dominate its surroundings.
Understanding this characteristic highlights the importance of early intervention and control measures to restore balance to your lawn.
Keeping Boreal Alopecurus at Bay:
After addressing an existing infestation, preventive measures are essential to stop future outbreaks. Here’s how to maintain a healthy lawn and reduce the risk of Boreal Alopecurus returning:
Routine Inspections
Regularly check your lawn for early signs of re-infestation.
Consistent Lawn Care
Stick to a comprehensive lawn care regimen that includes mowing, fertilization, and watering.
Mulching and Ground Covers
Consider using mulch or ground cover plants to help suppress invasive species growth.
Read: Women Arrreste Dover Necklace By Israelipolice- A Deep Dive!
Conclusion:
Boreal Alopecurus can pose significant challenges for homeowners striving to maintain healthy lawns. However, you can reclaim your yard from this invasive grass with prompt identification and effective management strategies.
By employing proactive lawn care practices and staying vigilant, you can ensure your grass remains lush, vibrant, and free from invasive threats.
FAQs:
What is Boreal Alopecurus?
Boreal Alopecurus, also known as Alopecurus alpinus, is a perennial grass species native to cooler regions. It is often recognized for its dense clumping habit and invasive potential in lawns and natural habitats.
How does Boreal Alopecurus spread?
This grass primarily spreads through its seeds, which are dispersed by wind and water. It can also expand its reach through rhizomes, allowing it to colonize new areas effectively.
What time of year does Boreal Alopecurus typically germinate?
Boreal Alopecurus usually germinates in early spring, taking advantage of the cooler temperatures before other grass species grow.
Can Boreal Alopecurus thrive in drought conditions?
While it prefers moist, well-drained soils, Boreal Alopecurus can tolerate some drought due to its deep root system, making it resilient in various climates.
What are the visual signs of Boreal Alopecurus infestation on a lawn?
An infestation may present as dense patches of green grass that grow taller than the surrounding turf. The characteristic seed heads resembling foxtails can also indicate its presence, especially in late spring to early summer.
How can I identify Boreal Alopecurus from other grass types?
Look for its tufted growth habit, deep green narrow leaves, and elongated seed heads. The smooth leaf texture and clumping nature are also key identifying features.
What are the best methods for controlling Boreal Alopecurus?
Effective control methods include manual removal, herbicide application, and promoting competition with desirable grass species. Regular mowing can also help manage its spread.
Is Boreal Alopecurus harmful to pets or livestock?
Boreal Alopecurus is generally not considered toxic to pets or livestock. However, it can create uneven and dense lawn patches, which may be less comfortable for animals to walk on.
What is the best time to treat Boreal Alopecurus in my lawn?
The best time to treat Boreal Alopecurus is during its active growth phase in early spring or early fall, when it is most vulnerable to control methods like herbicides.
Can Boreal Alopecurus affect soil health?
Yes, while its dense root system can help prevent soil erosion, the grass’s allelopathic properties can negatively affect soil health by inhibiting the growth of beneficial plant species and reducing overall biodiversity.
Read: 34 972982096: Guide To Enhance Data Management And Security!





